Is the Roman Empire Arise Again in the Last Days
6f. The Fall of the Roman Empire

Constantine the Smashing, 306-337 C.Eastward., divided the Roman Empire in ii and made Christianity the dominant faith in the region.
The invading army reached the outskirts of Rome, which had been left totally undefended. In 410 C.E., the Visigoths, led by Alaric, breached the walls of Rome and sacked the majuscule of the Roman Empire.
The Visigoths looted, burned, and pillaged their way through the urban center, leaving a wake of destruction wherever they went. The plundering continued for 3 days. For the starting time time in almost a millennium, the metropolis of Rome was in the hands of someone other than the Romans. This was the first time that the city of Rome was sacked, but by no means the terminal.
Constantine and the Ascent of Christianity
I of the many factors that contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire was the rising of a new religion, Christianity. The Christian organized religion, which was monotheistic ran counter to the traditional Roman faith, which was polytheistic (many gods). At different times, the Romans persecuted the Christians because of their beliefs, which were popular among the poor.

This 16th-century medallion depicts Attila the Hun, one of the most brutal invaders of all time.
In 313 C.E., Roman emperor Constantine the Dandy ended all persecution and declared toleration for Christianity. Later that century, Christianity became the official state religion of the Empire. This drastic change in policy spread this relatively new religion to every corner of the Empire.
By approval Christianity, the Roman state directly undermined its religious traditions. Finally, by this fourth dimension, Romans considered their emperor a god. Simply the Christian conventionalities in one god — who was not the emperor — weakened the authority and credibility of the emperor.
Constantine enacted some other modify that helped advance the autumn of the Roman Empire. In 330 C.E., he split the empire into ii parts: the western one-half centered in Rome and the eastern half centered in Constantinople, a city he named afterward himself.

Why Two Empires?
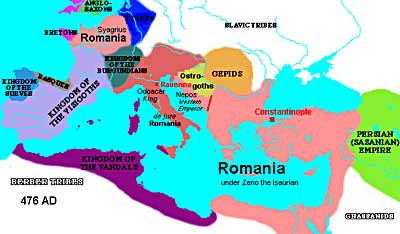
This map of the Roman Empire in 476 C.E. shows the various people who invaded and how they carved upwards the Empire.
In 324, Constantine's ground forces defeated the forces of Licinius, the emperor of the east. Constantine became emperor of the unabridged empire and founded a new capital metropolis in the eastern half at Byzantium. The city was his New Rome and was after named Constantinople (the "city of Constantine").

Empress Theodora was i of the near powerful women of late antiquity. She helped keep her husband, Emperor Justinian, in power and solidified the forcefulness of the Byzantine Empire in the 6th century C.E. as the western Empire collapsed.
Constantinople was advantageously situated for two reasons. Showtime, information technology was on a peninsula that could exist fortified and defended easily. Further, because Constantinople was located on the frontiers of the empire, imperial armies could respond more easily to external attacks or threats.
Some scholars also believe that Constantine established a new metropolis in society to provide a identify for the young religion of Christianity to grow in an environment purer than that of decadent Rome.
The western Empire spoke Latin and was Roman Catholic. The eastern Empire spoke Greek and worshipped nether the Eastern Orthodox branch of the Christian church. Over time, the east thrived, while the west declined. In fact, after the western part of the Roman Empire brutal, the eastern half connected to exist as the Byzantine Empire for hundreds of years. Therefore, the "fall of Rome" really refers only to the fall of the western half of the Empire.
Other fundamental problems contributed to the fall. In the economically bilious west, a decrease in agricultural output led to college food prices. The western half of the empire had a large trade arrears with the eastern half. The west purchased luxury goods from the east but had nothing to offering in commutation. To make up for the lack of money, the government began producing more coins with less silver content. This led to aggrandizement. Finally, piracy and attacks from Germanic tribes disrupted the flow of trade, especially in the due west.
In that location were political and military machine difficulties, as well. It didn't help matters that political amateurs were in control of Rome in the years leading up to its fall. Army generals dominated the emperorship, and corruption was rampant. Over time, the military was transformed into a mercenary army with no existent loyalty to Rome. Every bit coin grew tight, the regime hired the cheaper and less reliable Germanic soldiers to fight in Roman armies. By the terminate, these armies were defending Rome confronting their fellow Germanic tribesmen. Under these circumstances, the sack of Rome came as no surprise.
Goth Rockers
Moving ridge afterwards moving ridge of Germanic barbarian tribes swept through the Roman Empire. Groups such equally the Visigoths, Vandals, Angles, Saxons, Franks, Ostrogoths, and Lombards took turns ravaging the Empire, eventually carving out areas in which to settle downwardly. The Angles and Saxons populated the British Isles, and the Franks ended up in France.
In 476 C.Due east. Romulus, the last of the Roman emperors in the west, was overthrown by the Germanic leader Odoacer, who became the get-go Barbaric to rule in Rome. The club that the Roman Empire had brought to western Europe for thousand years was no more than.
dadeiteriabittem46.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.ushistory.org/civ/6f.asp
0 Response to "Is the Roman Empire Arise Again in the Last Days"
Post a Comment